As a rule, producing wire in protective gases, is a type of classical electric arc welding of metals due to the thermal energy of an electrical arc arising between the end of the electrode (wire) and the welded parts.
Since the arc resistance is slightly higher than the resistance of the electrode, the more significant thermal energy is released precisely in the plasma of the arc and places the nearby surfaces - parts and electrode, forming a welding bath. After crystallization and cooled volume of the resulting liquid metal, welded seam is formed, the most reliable of modern connections. Simplified welding process can be seen on video.
Principle and technology of semi-automatic welding wire
The distinctive feature of the considered type of welding is the two main components: a movable melting electrode (wire) and protective gas.
The protection of the electrical arc is necessary in order to prevent the use of the melted metal into contact with the environment, since this interaction (with oxidation of nitrogen and oxygen) leads to the formation of oxides and nitrites, the presence of which in the metal leads to the weld defects. For this purpose, protective gases in cylinders are used: argon, helium, carbon dioxide or mixtures thereof.
Schematically, the principle of semi-automatic welding can be seen in the figure. The movable wire under the voltage passes through the gas nozzle, melted under the action of the electric arge, but the preservation of the constant length of the arc provides an automatic feed mechanism. This is the principle of automation, and is chosen manually.
There is no gas use. In this case, self-defense is used ("(with the addition of manganese, silicon and other metals, which are deoxidizers), when combustion, forming around the protective environment. The process of such welding is clearly represented on the video.
The international standard is defined as GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding) and is divided depending on the protective environment used on Mag and MIG (in inert or active gas)
Composition of welding equipment
The welding set must include: a welding machine, a gas supply cylinder and a pressure of the weld current.
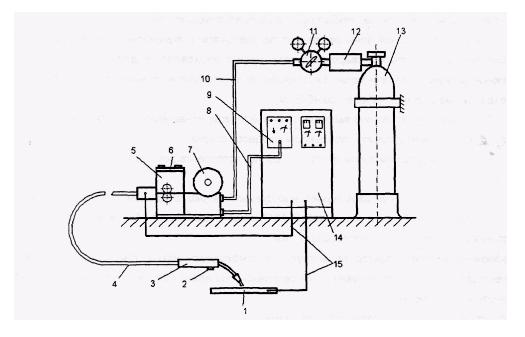
Installation of semi-automatic welding with melting electrode: 1 - detail; 2 - launcher; 3 - burner; 4 - Wire and gas supply hose; 5 - Wire supply mechanism; 6 - remote; 7 - coil with wire; 8 - cable; 9 - semiautomatic control unit; 10 - gas supply hose; 11 - Gas pressure reduction reduction reducing; 12 - heater; 13 - cylinder with gas under pressure; 14 - welding rectifier; 15 - cable.
The main parameters of semi-automated welding settings are within:
- Welding current (~ 40 - 600 A);
- Tension on the arc (~ 16 - 40V);
- Welding speed (~ 4 - 20 mm / s);
- Electrode wire diameter (0.5 - 3 mm);
- Length of wire departure (~ 8 - 25 mm);
- Feed rate (flow rate) electrode wire (~ 35 - 250 mm / s);
- Protective gas consumption (~ 3 - 60 l / min);
- Gas cylinder capacity (5 - 100 l)
Depending on the size and methods of moving, the semiautomatic can be divided into stationary, mobile and portable (knapsal).
Also welding machines differ from wire supply technology. The pushing type of feed, facilitating the weight of the burner, but limiting the length of the flexible hose with three meters is used. The pulling type allows the use of hoses to 20 meters, but the feed mechanism placed in the burner significantly increases its weight.
The burner is paid high attention. The nozzle and the conductive tip in its designs are quickly weathered with replaceable parts, and the quality of the seam produced depends on their state. During the welding, they require regular cleaning from sticking splashes, this process technology can be seen on the video. It is also recommended to closely monitor tightening and tip wear.
Materials used in semi-automatic welding
The electrode wire is used in a diameter ranging from 0.5 to 3 mm, depending on the thickness of the welded parts. Thinner allows you to maintain a stable burning of the arc and achieve greater inglow depth. Thick wire requires large welding current values, on average 100a per additional millimeter diameter.
The protective gas located in pressure cylinders is used both in pure form (inert Ag, HE and active CO2) and the composition of the mixture of these gases, depending on the welding mode and the type of the weldable material. The average consumption of carbon dioxide can be calculated, knowing the specific consumption of gas during the seam passage, adding additional consumption to it to perform preparatory and final operations.
Types and welding modes (electrode metal transfer)
In theory, several types of metal transfer are distinguished:
- with a short circuit of an arc or without it;
- finely, medium-, and large-scale;
- with sprinkling and without spraying.
This or that method is applied depending on the type and thicknesses of the materials of the materials, as well as the species used by the protective materials.
On the basis of these species, several welding modes are allocated:
- cyclic welding mode with short arc;
- point welding mode;
- mode;
- metal inkjet mode;
- the mode of continuous rotating metal transfer.
In practice, most often welding with the use of carbon dioxide and its mixtures is performed by a pulse-arc method at a constant current of reverse polarity. In some cases, welding is possible on alternating current. The reverse polarity in comparison with the straight is a smaller melting rate, but greater than the stability of the arc and a smaller spraying. Welding technique is convenient to understand from the video.
You can determine the necessary welding modes on the basis of data from table 2.
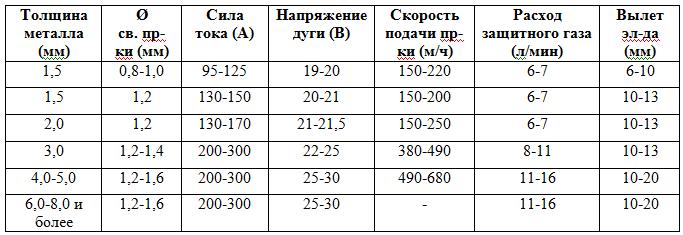
The current force is set depending on the diameter of the electrode and the thickness of the material. With its increase, the depth of the regulation and productivity in general is growing. As a rule, the current is regulated by the wire feed rate.
With increasing voltage, the opposite depth decreases, and the seam width and splashing increases. Set the voltage according to the power of the welding current.
The wire feed rate is directly related to the current power and is established on the basis of the requirements of the stability of the welding process. And the speed of welding depends on the thickness of the weldable material under the condition of preserving the quality of the applied seam. It is recommended to use narrow seams at high speed, as slow will lead to the spreading and inevitable defects.
The protective gas consumption is also directly dependent on the diameter of the wire used. You can improve protection or increasing consumption, or pressing the nozzle closer to the surface of the welding, as well as a decrease in welding speed. Excessive speed can lead to the output of the tip outside the protection and its oxidation.
The quality and stability of the welding process affects the departure of the electrode. With an increase in the departure deteriorates the stability of the arc, the metal is intensively sprinkle. Too small departure worsens visibility when conducting welding. The same applies to the release of an electrode, it will reduce the effectiveness of gas protection too much.
By summing up, we need to conclude that only the perfect set of all the parameters of the welding mode will make the process stable, and the seam and the result of the work is high quality.
Safety of work
In conclusion, a few words about safety technique. The technology of welding work is semi-automatic ways include the allocation of a special decade zone creating protection against access to foreign and protection against eye lesions with outbreaks of electrodes. There is a special video telling about TB standards.
The welder is obliged to apply personal protective equipment, before the start of work, check the serviceability of equipment and cylinders with carbon dioxide, and in case of detection, do not make any work without notifying the wizard. Welding equipment is a source of increased danger.