Materials based on several components, which determines their operational and technological characteristics. Composites are based on a matrix based on metal, polymer or ceramic. Additional reinforcement is performed with fillers in the form of fibers, whiskers and various particles.
Are composites the future?
Plasticity, strength, wide scope of application - this is what distinguishes modern composite materials. What is this from a production point of view? These materials consist of a metallic or non-metallic base. To strengthen the material, flakes of greater strength are used. Among them we can highlight plastic, which is reinforced with boron, carbon, glass fibers, or aluminum, reinforced with steel or beryllium threads. If you combine the contents of the components, you can obtain composites of different strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasives.
Main types
The classification of composites is based on their matrix, which can be metallic or non-metallic. Materials with a metal matrix based on aluminum, magnesium, nickel and their alloys gain additional strength due to fibrous materials or refractory particles that do not dissolve in the base metal.
Composites with a non-metallic matrix are based on polymers, carbon or ceramics. Among the polymer matrices, the most popular are epoxy, polyamide and phenol-formaldehyde. The shape of the composition is given by the matrix, which acts as a kind of binder. Fibers, strands, threads, and multilayer fabrics are used to strengthen materials.
The production of composite materials is carried out based on the following technological methods:
- impregnation of reinforcing fibers with matrix material;
- molding reinforcement tapes and matrix in a mold;
- cold pressing of components with further sintering;
- electrochemical coating of fibers and further pressing;
- deposition of the matrix by plasma spraying and subsequent compression.
What hardener?
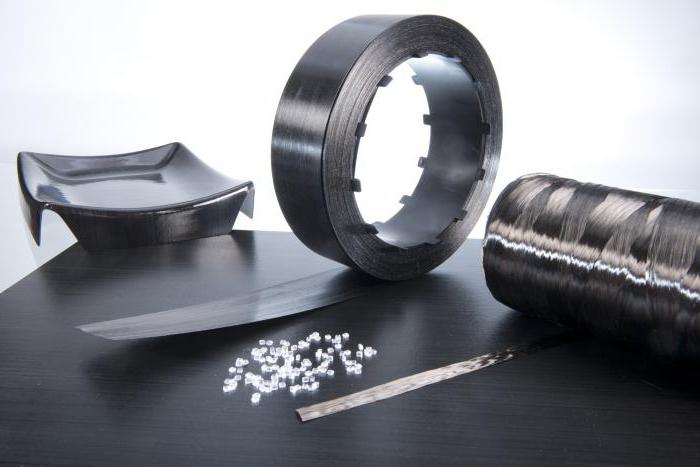

Composite materials have found application in many areas of industry. We have already said what it is. These are materials based on several components, which are necessarily strengthened with special fibers or crystals. The strength of the composites themselves depends on the strength and elasticity of the fibers. Depending on the type of reinforcement, all composites can be divided:
- on fiberglass;
- carbon fiber composites with carbon fibers;
- boron fibers;
- organofibers.
Reinforcing materials can be laid in two, three, four or more threads; the more there are, the stronger and more reliable the composite materials will be in operation.
Wood composites
Wood composite is worth mentioning separately. It is obtained by combining different types of raw materials, with wood as the main component. Each wood-polymer composite consists of three elements:
- particles of crushed wood;
- thermoplastic polymer (PVC, polyethylene, polypropylene);
- a complex of chemical additives in the form of modifiers - up to 5% of them in the composition of the material.
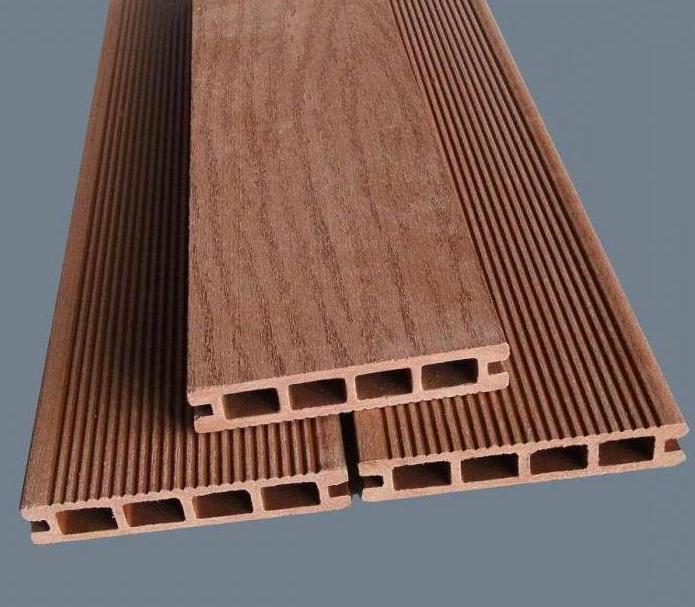

The most popular type of wood composites is composite board. Its uniqueness lies in the fact that it combines the properties of both wood and polymers, which significantly expands the scope of its application. Thus, the board is distinguished by its density (its indicator is influenced by the base resin and the density of wood particles), and good bending resistance. At the same time, the material is environmentally friendly and retains the texture, color and aroma of natural wood. The use of composite boards is absolutely safe. Due to polymer additives, the composite board acquires a high level of wear resistance and moisture resistance. It can be used to finish terraces and garden paths, even if they bear a heavy load.
Production Features
Wood composites have a special structure due to the combination of a polymer base with wood. Among materials of this type we can note chipboards of different densities, oriented chipboards and wood-polymer composites. The production of composite materials of this type is carried out in several stages:
- Wood is crushed. Crushers are used for this. After crushing, the wood is sifted and divided into fractions. If the moisture content of the raw material is above 15%, it must be dried.
- The main components are dosed and mixed in certain proportions.
- The finished product is pressed and formatted to obtain a marketable appearance.
Main characteristics
We have described the most popular polymer composite materials. What it is is now clear. Thanks to the layered structure, it is possible to reinforce each layer with parallel continuous fibers. It is worth mentioning separately the characteristics of modern composites, which differ:
- high value of temporary resistance and endurance limit;
- high level of elasticity;
- strength, which is achieved by reinforcing layers;
- Due to rigid reinforcing fibers, composites are highly resistant to tensile stress.
Metal-based composites are characterized by high strength and heat resistance, while they are practically inelastic. Due to the structure of the fibers, the speed of propagation of cracks, which sometimes appear in the matrix, is reduced.
Polymer materials
Polymer composites are presented in a variety of options, which opens up great opportunities for their use in various fields, from dentistry to the production of aircraft. Composites based on polymers are filled with different substances.
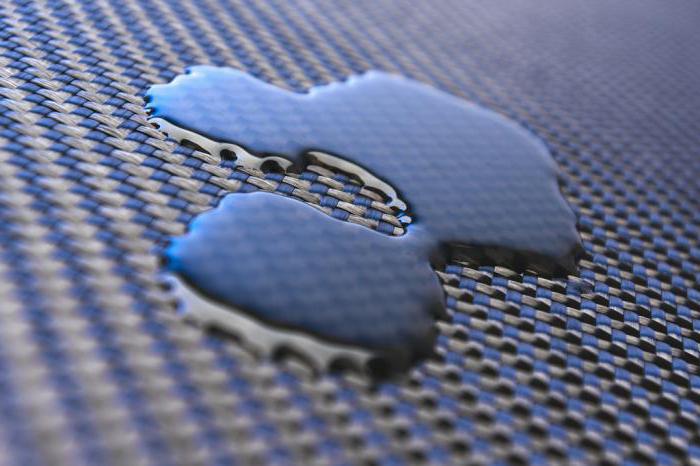

The most promising areas of use can be considered construction, oil and gas industry, production of automobile and railway transport. It is these industries that account for about 60% of the volume of use of polymer composite materials.
Due to the high resistance of polymer composites to corrosion, the smooth and dense surface of products obtained by molding, the reliability and durability of the final product increases.
Let's look at popular types
Fiberglass
Glass fibers formed from molten inorganic glass are used to reinforce these composite materials. The matrix is based on thermoactive synthetic resins and thermoplastic polymers, which are distinguished by high strength, low thermal conductivity, and high electrical insulating properties. Initially, they were used in the production of antenna radomes in the form of dome-shaped structures. In the modern world, fiberglass is widely used in the construction industry, shipbuilding, the production of household equipment and sports items, and radio electronics.
In most cases, fiberglass is produced on the basis of spraying. This method is especially effective for small- and medium-scale production, for example, hulls of boats, boats, cabins for road transport, and railway cars. Spraying technology is convenient and economical, since there is no need to cut the glass material.
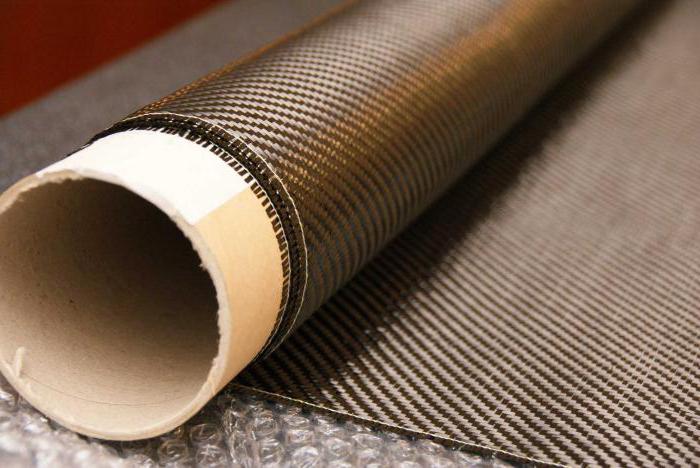
Carbon fiber reinforced plastics

The properties of polymer-based composite materials make it possible to use them in a wide variety of fields. They use carbon fibers as a filler, obtained from synthetic and natural fibers based on cellulose and pitches. The fiber is thermally processed in several stages. Compared to fiberglass plastics, carbon fibers have a lower density and a higher density while being light and strong. Due to their unique performance properties, carbon fiber reinforced plastics are used in mechanical and rocket engineering, the production of space and medical equipment, bicycles and sports equipment.
Boroplasty
These are multicomponent materials based on boron fibers introduced into a thermosetting polymer matrix. The fibers themselves are represented by monofilaments, strands, which are braided with an auxiliary glass thread. The high hardness of the threads ensures the strength and resistance of the material to aggressive factors, but at the same time, boron plastics are fragile, which complicates processing. Boron fibers are expensive, so the scope of boron plastics is limited mainly to the aviation and space industries.
Organoplasty
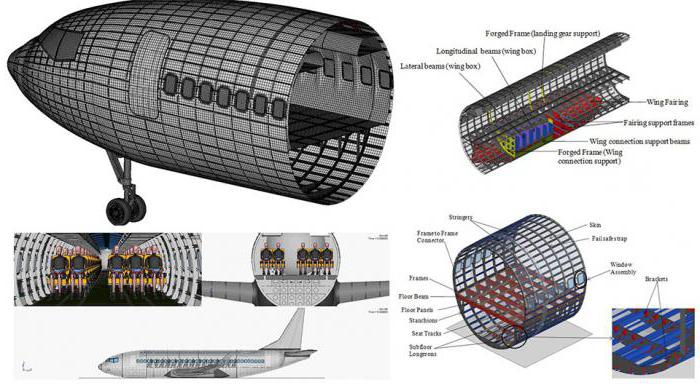
In these composites, the fillers are mainly synthetic fibers - tows, threads, fabrics, paper. Among the special properties of these polymers are low density, lightness compared to glass and carbon fiber plastics, high tensile strength and high resistance to impacts and dynamic loads. This composite material is widely used in such areas as mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, automobile construction, in the production of space technology, and chemical engineering.
What is the effectiveness?
Due to their unique composition, composite materials can be used in a variety of fields:
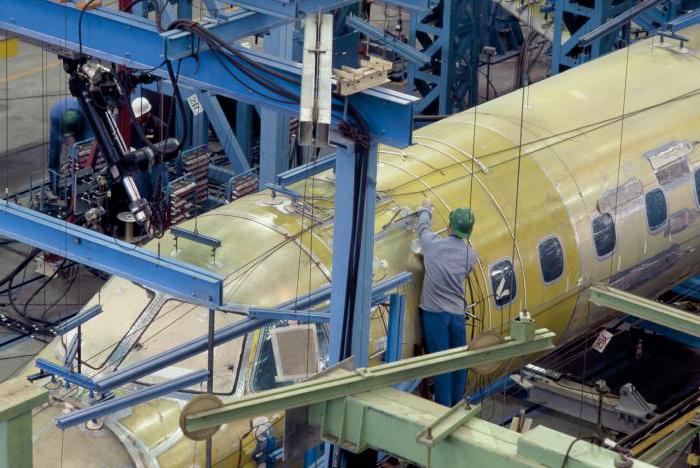
- in aviation in the production of aircraft parts and engines;
- space technology for the production of power structures of devices that are subject to heating;
- automotive industry to create lightweight bodies, frames, panels, bumpers;
- mining industry in the production of drilling tools;
- civil engineering for the creation of bridge spans, elements of prefabricated structures in high-rise buildings.
The use of composites makes it possible to increase the power of engines and power plants, while reducing the weight of machinery and equipment.
What are the prospects?
According to representatives of the Russian industry, composite materials belong to a new generation of materials. It is planned that by 2020 the volume of domestic production of products in the composite industry will increase. Pilot projects aimed at developing new generation composite materials are already being implemented across the country.

The use of composites is advisable in a variety of fields, but it is most effective in industries related to high technology. For example, today not a single aircraft is created without the use of composites, and some of them use about 60% of polymer composites.
Thanks to the possibility of combining various reinforcing elements and matrices, it is possible to obtain a composition with a certain set of characteristics. And this, in turn, makes it possible to use these materials in a variety of fields.