Reinforcing steel is not officially called that way: if you study GOST 5781-82, you can find out that the correct name sounds like "hot-rolled for reinforcing concrete structures". However, the name turned out to be too long, so in a professional environment it was quickly shortened to a simple "armature". It is clearer, simpler and faster.
general information
It is customary to distinguish several classes of reinforcement. The division is based on the following criteria:
- periodic profile;
- mechanical parameters.
Reinforcing steel is of the following classes:
- AIII.
For several years now, the market has a rather high demand for the A500C class of reinforcing steel. If you study GOST 5781-82, you will not be able to find descriptions similar to it in its parameters. These products are manufactured in accordance with the following standards:
- STO ASChM 7-93;
- technical conditions.
Such a system of standardization, according to which hot-rolled reinforcing steel of a periodic profile is grouped into categories, was introduced by enterprises working in the field of ferrous metallurgy. They are united into a single association, which has taken upon itself, among other things, the development of rules for the production of goods.
A special case
The described reinforcing steel A500C is not the only exception in the world of hot-rolled products. Also, the AI class deserves special attention, which in GOST is usually designated as A240. The key feature is the sleek profile. Steel 3 SP (PS) is used as a raw material for the production process. Diameter and deviations from it for any products with a smooth profile are regulated by GOST 2590-88. This normative document also specifies the rolling accuracy for general cases.
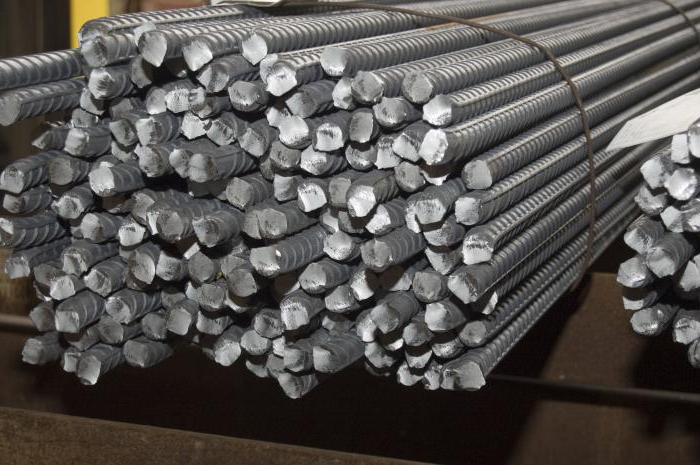

Reinforcing steel smooth is produced in the following formats:
- rods;
- bays.
In skeins, you can find sizes from 6 to 14 mm (step - 2 mm). The choice of reinforcement in bars is somewhat wider. The smallest possible diameter is 16 mm and the largest available is 40 mm. From 16 to 22 mm, the pitch is 2 mm, from 25 to 40 mm it increases to three.
How and why?
Reinforcing steel grade A240 is necessary in construction and other areas where reinforced concrete structures are used, as it is used for their reinforcement. Some experts call this category of materials "loop", since it is customary to use reinforcement to form loop-like elements that reinforce reinforced concrete products. This is most important when the element stands out from the main plane of the structure. Hot rolled reinforcing steel A1 is suitable for creating elements that simplify the loading of finished blocks, transportation and unloading. In addition, it is easier to connect different elements to each other directly on the construction site.
Rebar grade AI, like round, is required for a wide range of designs. When using it, they make:
- fences;
- furniture;
- railings.
Circle and metal reinforcement A1, if they are made in accordance with specialized standards, are used as raw materials: wire can be drawn from them. Production of profiles is allowed:
- periodic;
- smooth.
If the reinforcement plant has the appropriate equipment, then A1 steel can be used for the manufacture of various products on lathes or milling machines. The material is processed mechanically.

Paying attention to standards
Tells about what the reinforcing steel should be, GOST 5781.82. According to the standards, carbon in the metal composition can be no more than 0.3%, only then the product is applicable for reinforced concrete. Reinforcing bars are used both for previously stressed raw materials and for conventional ones.
If pre-treated and stressed reinforced concrete is used, then the reinforcement is chosen one that can cope with the rather serious loads inherent in this environment. As a rule, the stress is quite large, which requires that the metal reinforcement be of increased strength and is made strictly from reliable steel. If wire is used, then high demands are also placed on its strength.
If hot rolled reinforcing steel will be used in stress-free structures, then ordinary raw materials can be used. The following steel grades are relevant here:
It is customary to take steel with carbon content for prestressing:
- medium;
- high.
Steel reinforcement, thermally treated to increase the strength parameters, can also be used.
Steel: which one shall we take?
To make high-quality reinforcing steel, GOST 5781.82 recommends taking reliable steel:
- carbonaceous;
- low alloyed.

There are several grades applicable to different types of the mentioned material. As a rule, the customer, when sending an order to the valve plant, indicates from which raw material he wants to see the finished product. If the manufacturer does not receive such recommendations, then the manufacturing enterprise independently decides in favor of the optimal option for a specific type of product. In particular, the following brands are commonly used for the A800:
- 22Х2Г2АЮ.
- 22X2G2R.
- 20Х2Г2СР.
What else is important?
When creating unstressed reinforced concrete structures, you should choose classes from the first to the third, and higher ones will come in handy if the structure has undergone prestressing.
If it is necessary to work at low temperatures, and the object will be further operated in extreme conditions, then such a brand of reinforcement is more suitable, which is distinguished by a reduced percentage of carbon. Alternatively, you can select options for raw materials that have undergone additional high temperature processing.
But if it was decided to use wire as a reinforcing material, then it is better to give preference to one in which carbon is either completely absent or its content does not exceed 0.8%. This material is characterized by increased strength - up to 180 kgf / mm 2 inclusive. Such parameters are provided:
- high temperature processing;
- riveted.
Carbon and material quality
It regulates from what raw materials construction fittings should be made, GOST 5781-82. In particular, the percentage of carbon has a fairly strong effect on the final parameters of a reinforced concrete product, on its durability and reliability. The more carbon is contained in the metal, the higher will be the hardness inherent in the reinforcement, but at the same time, the fragility increases. In addition, it is very difficult to weld high-carbon steel, often the result is not of high quality, which affects the reliability of the entire structure as a whole.
The percentage of carbon allows the following classification to be introduced:
- low-carbon steel reinforcement, where this compound is contained in an amount of not more than a quarter of a percent;
- with an average level of content - from a quarter of a percent to 0.6;
- with a high content, ranging from 0.6 to 2%.
How can we improve it?
In order for the reinforcing steel to have the best quality, additional components can be added to the alloy. It is customary to use as alloying components:
- tungsten;
- vanadium;
- chromium;
- nickel.

In some alloys, only one or two additional components are added, in others - a mixture of 5-6 metals. This allows you to get high quality with high performance:
- strength;
- hardness;
- corrosion resistance.
To obtain, silicon and manganese can be included in the raw material. Depending on how many additives are contained in the substance, it is customary to talk about the material belonging to one of the following classes:
- low-alloy reinforcing steel containing no more than five percent of inclusions;
- medium alloyed, in which the amount of additives varies in the range of 5-10%;
- highly alloyed, one tenth or more consisting of additional components.
"What's in a name?"
Reinforcing steel is not just steel, but also a large number of other chemical components. You can find out what inclusions are in the material from the name. Standards have been developed for the designation of certain additives in the name of the material. Examples:
- X is chrome.
- C - zirconium.
- T is titanium.
The numbers are written after the mark. They reflect how much carbon a material contains. Hundredths are indicated. Then they write letters. They designate a chemical element, after which it is indicated how much of it is contained in the composition of the reinforcement. If no figure is given, it can be concluded that this substance is included in a volume of less than one percent.
Example: "reinforcing steel 35GS" stands for steel, which contains carbon in a concentration of 0.35%, as well as silicon and manganese, but the percentage of both components is insignificant, therefore there are no specified data (they are present in a volume of less than a percent of the total amount of material).
What to demand and wait for?
According to current standards, reinforcing steel must be:
- easily weldable;
- plastic;
- durable.

Strength is usually understood as the ability of reinforcement to withstand destructive loads of the external environment. External influences can stretch the metal and bend, twist and squeeze, cut. For each of the types of loads, separate strength indicators are distinguished. Reinforcement is more often used in conditions where tensile loads are high, so this value should be paid attention to first. To assess how the reinforcement is able to resist tension, you need to evaluate:
- fluid limit;
- breaking resistance.
Plasticity is a parameter that reflects the adaptability of a material to external loads that try to change the shape of the product, its section. If the reinforcement in such conditions retains its initial parameters, then after removing the load, it can return to its original state or save the obtained changes. Plasticity is expressed in elongation at break, bend angle, and the number of bends remaining after cooling the metal.
Weldability is an indicator that reflects the ability to qualitatively bond with other materials when using a particular welding method. This parameter is determined by:
- metal composition;
- by smelting;
- the size of the rods in the section;
- connecting features;
- plasticity.
Mechanics and reliability
The above parameters allow us to talk about how good the mechanical parameters of the steel are. It is on their basis that technical characteristics and indicators are distinguished.
An important feature of the reinforcement is its temporary resistance. To determine it, as well as to identify how large the fluid limit, how large the steel elongation can be relative to the initial value, special tests are carried out in production: tensile testing machines designed for this task are used.
The work is carried out as follows: when the machine is started, the load on the placed sample gradually increases. In this case, the armature is in a rigid fastening system, which does not allow the specimen to "slip away". The mechanisms try to lengthen the rod longitudinally by deforming it. The indicators taken from the reinforcement allow you to form a tension diagram (the scale is set arbitrarily).
Technical features
Straight sections of the diagram reflect loads such that the sample does not deform. With increasing loads, a proportional increase in length can be seen, allowing conclusions to be drawn about the reliability of steel and the ability to resist external influences. The limit value of the load applied to the test specimen is set in advance. Upon reaching this value, the influence of mechanical force is also gradually reduced.

In the best case, the rod, stretched under the influence of a large external force, returns to its original state when the loads are removed. This ability is due to the elasticity of steel. It should be understood that the elastic zone for metal has certain limitations. When the indicators exceed these limits, the return to the original values will become impossible. When such a boundary indicator is identified, it is said that the elastic limit has been reached.
If we test the reinforcement made in accordance with the current GOST ST3 steel, then it will be possible to obtain parameters close to the following:
- - 2 460 kgf / cm 2;
- elongation - 25;
- tear resistance in a given time interval - 4000 kgf / cm 2.
Parameters and scope
Reinforcement with high strength values usually costs more than low-quality material. At the same time, practice shows that the use of such a material can achieve significant savings, since the reinforcement of reinforced concrete structures requires a more economical consumption of metal.
Pay attention to the plasticity of the reinforcement: there are certain boundaries, which are highly undesirable to go beyond. When this parameter drops below a certain level, it is impossible to use rolled products at full strength. A structure made using such consumable raw materials becomes fragile and can collapse unpredictably under the influence of external factors. There is another risk associated with a decrease in the ductility of the metal: the probability of brittle fracture increases already at the stage of reinforcing reinforced concrete structures.
Impact on steel samples
To improve the performance of the reinforcement, they resort to various technologies of external influence. In particular, the practice of thermal hardening is widespread. In this case, the strength of the material doubles, and sometimes more. This is most applicable for low-alloy, carbon compounds. But the cost of the material increases by only 10-12%. Thermal hardening shows the best performance relative to mechanical hardening, but for its implementation you need to have serious modern equipment and a team of highly qualified specialists. Even the smallest errors in the technological process greatly affect the quality of the final product (and the reputation of its manufacturer).

Mechanical hardening is achieved by using:
- winches;
- hydraulic jacks;
- profiled rolls.
The latter are needed to flatten steel. During hardening, it is possible to achieve plastic deformations, due to which the strength increases by 50% relative to the initial value.
The most popular - what is it?
Traditionally, the most demanded in the metal rolling market is reinforcement of 8 mm in diameter. It belongs to the third class and is produced in coils, skeins, rods. 8 mm is the parameter of the average diameter of the building material. The production of such fittings must comply with GOST 30136-95. Reinforcement produced by coils is called "wire rod" by specialists.
The 8 mm armature is made from low carbon steel. Grades CT0, CT3 are used. In the manufacturing process, there are two (sometimes one) cooling stages, which makes it possible to achieve high indicators of material reliability. Wire rod in skeins is a wire.
Armature A3 - steel with a circle in cross section. It is necessary for the subsequent production of wire, springs. Raw materials are indispensable in the production process of construction cold-drawn reinforcement.
Production and sales
Reinforcement 8 mm is usually made on wire-section machines from raw materials corresponding to GOST 380. This is a standard technology, assuming the presence of bar steel, processed by the gross system. On machine tools, the material is rolled and stretched, heated and cooled. Depending on the characteristics of a particular product, it will be cooled naturally or forcibly.
On sale, such a product is present both in running meters and in large skeins (for wholesale buyers).

Why is this needed?
Reinforcement 8 mm is indispensable for the construction of reinforced concrete and metal structures. Wire rod is thin enough, therefore it is used in the manufacture of nets, frames, ropes. The armature is effective as a base for staples. It is used to strengthen building structures. The specific option is chosen by analyzing the operating conditions of the building, on the basis of which a decision is made in favor of a particular brand.
Reinforcement is more often used as a raw material for the manufacture of other construction products, and not as an independent material. If wire rod is needed to produce nails, cables, then you need to control the evenness of the products: rough surfaces are unacceptable, this will significantly reduce the strength of the finished product. In the manufacture of thick reinforcement, staples, the requirements for surface smoothness are not so significant. The reinforcement used for the arrangement of load-bearing walls cannot contain cavities or cracks filled with air. If 8 mm diameter reinforcement is purchased in rods, quality control involves tracking the identity of the products.
Some features
It should also be noted that reinforcement having a circular periodic profile is usually equipped with longitudinal ribs. Helical protrusions run across the rods, laid along a line with three starts. If the diameter of the bar is up to 6 mm, then the protrusions can run along the helical line in one pass. For 8 mm, two leads are allowed.
Armatures classified as the third class are:
- usual;
- special.
It is designated as A300 and Ac300, respectively. For such raw materials, protrusions are characteristic, in which the approach on both sides of the profile is uniform. Here, the lines also go with a screw. But for the A400-A1000, a prerequisite is: right-handed entry on one side, and left-hand on the other.

Displacements of the screw lugs are possible. This parameter is not standardized according to the current GOSTs.
Another distinctive feature is the production of A800 steel. The following brands can be used for it:
- 22Х2Г2АЮ.
- 22X2G2R.
- 20Х2Г2СР.
In this case, the features of the final product are usually regulated by the customer's requirements.
- A400C.
- A500S.
Both of them are suitable for strengthening reinforced concrete structures and replace the previously widely used A-III. These are manufactured taking into account the requirements specified in GOST 5781-82.