More than 4 hundred years have passed since the famous French architect Francois Mansart proposed using the attic space as a living space. But even today his invention is in high demand, especially among those people who want to make the most of the available living space without making major changes to the project.
Pros and cons of brick houses
A brick house is a beautiful permanent structure that can be used for summer holidays and for permanent residence. This material provides almost unlimited design and architectural possibilities, is extremely durable and versatile, and adapts to the owner’s needs.
Brick houses are considered one of the most reliable, but their construction is quite expensive.
Like any other type of building, brick houses have their strengths and weaknesses. The advantages of brick houses include:
- The ability to retain heat for a long time in severe frosts and keep cool on hot days.
- High fire safety - a brick building will never catch fire like a wooden one.
- The design is also not susceptible to exposure to snow, hail, rain, sudden temperature changes, or other atmospheric surprises.
- Versatility in terms of style and architectural solutions.
- Good environmental friendliness.
A brick house can be decorated in any style - from classic to empire.
Flaws:
- High-quality brick is expensive, and low-quality brick has low performance indicators.
- The mass of material is impressive, so you will have to build a reliable, powerful foundation for the house.
- Brick walls need finishing.
It is better to live in ready-made buildings permanently, and for temporary residence use wooden or other structures. Read more about what is best to build a house from.
If you do not want to finish the walls, use facing brick instead of regular brick. This material looks attractive, but also costs a lot.
Design
Before you start construction, draw up a plan for your future home. In this case, the attic must be designed strictly in accordance with the current design features of the room and the layout of engineering systems. The attic window should account for about 1/8 of the entire area of the room. Design two-thirds of the space in the room in such a way that the ceiling height in them is 2.4 m. For an example of planning and building a house with an attic, see.
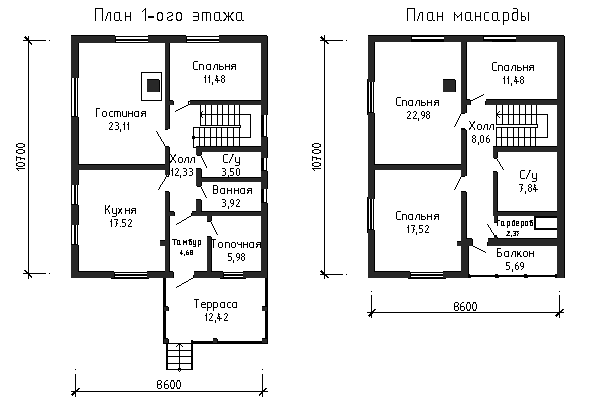
Layout of a building with an attic
When designing a brick house with an attic, consider your financial capabilities. To reduce the cost of the project, hire outside specialists only to perform those types of work that you cannot do yourself.
The attic solves two problems - practical (increases usable living space) and architectural (changes the appearance of the building).
Other features that need to be taken into account when drawing up a project:
- The intersection point of the facade and the roof should be at a height of 1.5 m from the floor level.
- Insulate the roof together with the insulation of other rooms.
- Immediately think about the location of the heating system - brick absorbs water, and you must ensure an optimal balance between temperature and humidity levels.
- Consider the topography of the area where you are building - the soil is examined for the degree of freezing and the level of groundwater. If the soils are wet and weak, it would be best to make a pile-screw foundation.
- When calculating the number of rooms, take into account the composition of the family and your love for guests - you need to have enough space for everyone.
A summer brick house can be anything - the main thing is that you feel comfortable in it. A building for year-round use must have insulated floors.
Construction stages
The first thing you will need to do is decide on the type and quantity of materials. Plain brick is cheaper than facing brick; from a constructive point of view, it can be hollow or solid. When choosing, pay attention to such indicators as thermal conductivity, frost resistance, strength, and water absorption. The amount of material depends on the area of the future room.
During construction, you can use not individual materials, but their combinations - for example, make a house out of brick and an attic out of wood.
Selecting and pouring the foundation
A house starts with a foundation. For brick houses, slab, pile and strip foundations are usually used. Let's consider their features.
Strip foundations are in high demand in modern construction because they can withstand significant loads created by concrete structures. It can be built under internal and external walls.

The strip foundation can be recessed or shallow - for brick houses the first solution is usually used.
Types of strip foundations - prefabricated and monolithic, both options are suitable for arranging basements and basements. From a constructive point of view, the monolithic type foundation under consideration is a single reinforced concrete structure; stone and concrete blocks are used to create prefabricated solutions.
The main advantage of the strip base is the high speed of construction.
Procedure for pouring the base:
- The area is prepared - the turf is cut and markings are made.
- A pit or trench is being dug - the second option provides for the possibility of arranging a basement or plinth, but the first does not. The bottom is leveled, after which the angular depth markings are checked using a theodolite.
- The trench or pit is wetted with water, then a sand or gravel fill is created. The optimal thickness of the mixture is 0.2 m, its compaction is carried out using a vibrating plate. When the cushion is compacted, waterproofing is laid and lightweight concrete is poured. They work with prefabricated structures in a similar way, only the cushion is placed directly under the concrete blocks.
- Formwork is knocked together from boards up to 5 cm thick, which are then fastened together using spacers. The walls of the structure are made vertical.
- A frame is created from reinforcement. Take rods with a cross-section of up to 1 cm, fasten the required number of sections by welding, then lay the frame in the trench on supports.
- Pour concrete into the formwork - the work is carried out in stages and involves uniform distribution of layers up to 0.2 m in thickness. Laying is carried out in several stages, after each stage the concrete is vibrated.
The foundation will be strong if you use a solution of medium consistency to create it.
If the soil in the area is crumbling, opt for a pile foundation, which can normally withstand even very significant loads. Piles ensure the most uniform redistribution of loads, with the bulk of them falling on dense soils lying at a considerable depth. The main disadvantage of this solution is its complexity.
Arranging a pile foundation on solid soils allows you to save building materials and reduce the volume of excavated soil.
The procedure for arranging a pile foundation is as follows:
- Prepare the site, as in the previous case, mark the places where you will drill the piles.
- Use a drill to make holes for the piles.
- Weld a frame of reinforcing bars. The frame should rise approximately 0.3 m above the ground surface.
- Pour some gravel and sand onto the bottom of the well, lower the frame of rods inside, and fill it with solutions. To obtain a monolithic foundation, the concrete will need to be leveled.
- Weld the frame base for the grillage, tie the frames of the grillage and piles. For the reinforcing base of the structure, assemble the formwork.
- Pour concrete - optimally in layers, in several stages.

Before starting work, you must make markings. This is especially true for uneven areas with complex terrain.
When the foundation dries and gains strength, all that remains is to waterproof the grillage.
The piles are placed at a certain distance above the ground, and metal pipes of a given diameter are used to construct the formwork.
The last type of foundation used for the construction of brick houses is slab. It looks like a solid reinforced concrete slab that can normally withstand the loads from the building. Neither vertical nor horizontal movements of the soil affect the integrity and strength of the foundation. The following types are distinguished:
- floating - the base lies in the ground at a depth of up to 0.5 m;
- not buried - the base is not dug in, but installed on the surface of the earth;
- recessed - the bottom of such a foundation is located below the soil freezing level.
The most popular type of slab foundation is shallow.
To create a slab base, you need a lattice or solid slab, which consists of slabs and beams. Work order:

In the first few days, the slab foundation needs to be watered. Otherwise it may crack
- Preparation is carried out in the same way as for other types of bases.
- Excavation of soil to a depth slightly greater than the thickness of the foundation being built. Crushed stone or sand is poured into the pit, after which the cushion is leveled and compacted. A layer of lightweight concrete is poured on top.
- Creation of high-quality hydro- and thermal insulation. Roofing felt is laid on the concrete, and foam is laid on top of it.
- The formwork is knocked down along the contour of the base - to create it, it is best to use boards up to 5 cm in thickness.
- The frame is made - it is welded from metal rods.
- Concrete is being poured - one go will be enough. The poured mass is tapped and left to harden.
The slab base is ready.
Walls and floor
Before you start building walls, decide what type of masonry you will use. The most popular options:
- With metal mesh. The mesh is laid every 5-7 rows.
- Well - masonry with voids that are filled with foam or expanded clay. This approach helps to increase the thermal insulation characteristics of the material.
Methods of laying bricks when building walls are well and with metal mesh.
First, the material is laid in the corners of the load-bearing walls. Please note that the appearance of the building and its durability depend on the quality of installation of the material. When forming corners, you need to lay 5-10 bricks in height. How correctly you do everything can be checked with a level and plumb line. The more often checks are carried out, the lower the risks of distortions.

Layout of house walls
Wall laying stages:
- Prepare the cement mortar - this should be done in small portions and prepared as needed.
- Apply the solution to the desired location and level thoroughly. Excess is removed with a trowel.
- Lay the brick on the mortar, tap it with a trowel to ensure a tight fit of the brick. The ideal distance between rows is 12 mm.
- Narrow the rows when laying - either due to the thickness of the mortar, or using pieces of brick.
If you plan to plaster the walls, leave some space in the joints. In cases where the work is carried out immediately with facing bricks, the jointing will need to be done carefully and beautifully, immediately filling the entire space.
At the stage of wall construction, it is necessary to provide for the presence of door and window openings - voids of the specified parameters are left for them. When you reach the planned height of the opening, lay lintels - made of wood, reinforced concrete or metal.
The width should be the same as the thickness of the wall, and the length should be 50 cm greater than the width of the opening. The ends of wooden lintels are protected with roofing felt and treated with a primer; metal products are treated with anti-corrosion compounds.
The reliability of the attic (and it will have to withstand significant wind loads) depends on the quality of the rafter system. It is made from beams of considerable length and width. First you will need to lay the mauerlat - the lower outer support of the rafters made of logs or timber. The most reliable section is considered to be 20*20 cm with a distance between logs of 1 m.
Floors in a brick house are laid:
- on the logs;
- on the ground;
- on floor slabs.
Be sure to take care of high-quality insulation, otherwise in the future you will heat the air. The most popular heat insulators are polystyrene foam, basalt wool, and polystyrene foam. For exterior decoration, materials such as lining, exterior plaster, siding (vinyl, metal), and natural wood are usually used. Select interior decor taking into account personal wishes and financial capabilities.
It is best to insulate the walls of a brick house from the outside.
Roof
The roofing process consists of several stages:
- project development and selection of roofing material;
- installation of a rafter system (usually used to create it);
- installation in increments of 80 cm for slate, 35 cm for metal tiles, for a bitumen roof the sheathing is made continuous;
- waterproofing;
- laying roofing material, installing decorative elements;
- vapor barrier and insulation (if necessary).

Mansard roof diagram
To supply water from a source, it is most convenient to use automatic pumping stations.
Water pipes are always laid below the freezing level of the soil and equipped with shut-off valves. In unheated rooms and places where water supply enters the house, they need to be insulated. Plumbing fixtures are installed according to the manufacturer's instructions. A bathroom can consist of only a toilet or a bath and toilet. Do not forget about the need to create a wastewater treatment system.
Electrics
Installation of wiring in a private brick house begins with preparation - drawing up wiring diagrams, marking, and punching work. Immediately decide on the place where the wires and cables will be inserted and where the distribution board will be installed.
Then it will be possible to prepare the installation and electrical diagrams, mark the installation locations of electrical appliances, sockets, switches, lamps, junction boxes and other elements of the system. After marking, wiring route diagrams are prepared.
Each group or individual socket needs its own circuit breaker with a power corresponding to the wiring cross-section.
All wiring lines for connecting sockets and lighting groups are connected to a panel with auto switches. The permissible current value for the conductor is determined taking into account its cross-section, cooling conditions (closed or open wiring), and material. The distribution boxes must be left freely accessible - this will allow you to monitor the condition of the connections during their operation.
Video
For more useful information about the technology of building a brick house, watch the video
Conclusion
A brick house with an attic is a permanent structure that is suitable for year-round use. The reliability of the building depends on the correct choice of foundation, adherence to wall laying technology, and the installation of a high-quality roof. If you plan to use the attic as a living room, then you need to take care of its insulation and waterproofing. Read more about ways to insulate an attic. Please note that construction work is labor-intensive and time-consuming.
The article will tell you about the construction of a foundation made of screw piles for a house with an attic.
Nowadays, owners are increasingly building houses with an attic. However, the design of the attic floor has nuances.
Firstly, the roof is also an outer wall. Therefore, it is important to think over a competent rafter system and take care of the installation of steam, hydro and thermal insulation of the roof.
Secondly, the useful volume and layout of the attic depend on the shape of the pitched roof: the steeper the slope, the larger the area. Areas with the lowest ceilings are, as a rule, simply excluded from the living space.
The approach to designing and installing the foundation of a house with an attic differs little from the design and installation of foundations for other types of objects.
Determination of soil conditions of the construction site
The foundation transfers the loads from the building to the soil underneath. Therefore, in order to design it, it is necessary to have accurate data on the ground conditions in the construction site.
The geology of the site allows:
identify dangerous geological objects and processes (if they exist) - suffusion, karst, quicksand;
identify different soil conditions that may occur even within a small area.
This indicates that building without knowing anything about the soils on the site is a dangerous undertaking.
Specific ground conditions are taken into account when assigning barrel length, blade spacing, pitch, pitch angle, and blade configuration (not to be confused with diameter).
The corrosive aggressiveness of soils (CAG) at the construction site affects the purpose of the steel grade (for more details, “”) and the thickness of the wall of the barrel and blade (for more details, “”). Only compliance of these parameters with the CAG degree will make it possible to achieve compliance of the service life of the building with the requirements of regulatory documents (GOST 27751-2014 “Interstate standard. Reliability of building structures and foundations. Basic provisions”).
When the service life calculation is completed, the residual thickness must be checked to ensure compliance with the design loads.
After the piles are immersed to the design depth, control measurements of the torque value (TMC) are performed. Although a similar procedure (test screwing) is often considered as an independent study, this is not entirely correct. The results, firstly, will be highly dependent on the time of year, and secondly, the method does not provide any information about the properties of the soil under the pile.
Therefore, determining the magnitude of the torque (which indirectly occurs during test screwing) should only be a confirmation of information about soil conditions, but not a method for determining their bearing capacity.
Collection of building loads
Not only the own weight of parts of the structure (permanent loads), but also the effects from people, furniture, wind, snow (temporary loads), which are often neglected, must be taken into account. Only by summing them up can one obtain objective information about the loads on the foundation.
A detailed calculation scheme with examples is contained in the article “” and is suitable, among other things, for determining the bearing capacity of a foundation made of screw piles for a house with an attic.
How to arrange piles taking into account the impact of different loads on the foundation
Different parts of the structure transfer loads of different magnitudes to the foundation:
under critical components of the structure;
under load-bearing walls;
under curtain walls, floor joists.
How the pile will take loads from the structure is influenced by:
soil conditions of the site;
number, diameter and configuration of blades.
The durability of the structure and its compliance with the requirements for rigidity and strength will primarily depend on the wall thickness and diameter of the barrel.
Therefore, piles in the foundation should be placed, as a rule, in this way:
This arrangement will allow the safety factor to be evenly distributed throughout the entire base, which means it will increase its service life and reliability.
Grillage of a pile-screw foundation for a house with an attic
The foundation for a house with an attic is always calculated individually. So that we can calculate its cost for you, provide data about the object (wall structure, number of storeys, etc.) and geological survey data or sign up for a geologist to visit you.Nowadays, houses with attics are increasingly being built. An attic or attic floor is a room in the attic space, the walls of which are formed by the surfaces of the roof. The first to use this design was the Frenchman Francois Mansart back in the sixteenth century. Who would have thought that they would become so popular nowadays.
A house with an attic has its own characteristics compared to a simple house. The main one is the shape of the roof. For houses with an attic, gable, hip and hip roofs are mainly used.
What attracts people to houses with attics? Firstly, it’s beautiful, and secondly, it’s economical; you don’t have to build walls on the second floor. Also, such rooms have fewer windows than regular ones and this will reduce your costs.
Such houses can be built from any building materials: brick, wood, concrete. Thanks to different materials, a house with an attic can resemble either a castle or a fairy-tale tower.
Any construction begins with the foundation of the building. Let's figure out which foundation for the attic is better.
In the construction of private cottages, the following types of foundations are more often used:
- Tape;
- Columnar;
- Pile;
- Slab.
Each of them has both disadvantages and advantages for use as a foundation for a house with an attic.
The strip foundation completely follows the line of the load-bearing walls of the building. Such a foundation is made in the form of a concrete strip buried in the ground. These concrete strips are often laid on so-called concrete pads, thereby achieving greater stability.

A strip foundation is suitable for a house with an attic or a two-story house as it can withstand heavy loads.
The columnar foundation is used for the construction of light and small buildings and therefore it is not suitable for the construction of houses with an attic.
Pile foundations are mainly used on slopes and in very soft soil. It consists of piles installed vertically into the ground. Piles can be made of reinforced concrete, wood and asbestos.
Slab foundation is the most expensive type of foundation. However, it is worth the money spent on it. Such a foundation is particularly strong, since the load is evenly distributed over the entire soil area.
Foundation for a house with an attic
The foundation for a house with an attic is selected and calculated, taking into account the condition of the soil, the proximity of groundwater, the depth of freezing and the magnitude of the load.
It is best to order a foundation design from a design organization.
Mostly we neglect this and follow the advice of builders (good if they are professionals) or the experience of neighbors who have recently completed construction.
If the house is not located on a slope, a monolithic slab foundation is suitable for any type of soil.
A cheaper option is a strip foundation, which is a well-reinforced reinforced concrete strip located on a sand bed and following the contours of the building.
The choice of foundation type also affects whether the house will have a basement or not.
If you do not plan to make a basement under the house, then a shallow strip foundation would be appropriate. It is done with monolithic concrete in one day, so that there are no seams, and reinforced with 12mm reinforcement.
The base of the foundation is made of compacted coarse sand.
In view of all of the above, we can conclude that the foundation is one of the most important elements of your home. The strength and durability of your home will mainly depend on it.
It’s better not to skimp on the foundation and use the best materials you can afford. Because any miscalculations and mistakes when laying the foundation can result in serious costs for their alteration when the house is already built.
As they say, it’s better to measure seven times and cut once.
You can see the main mistakes when laying a foundation in this video:
Read also:
Maxim Sobolev. I want to build a house with an attic, essentially a two-story 6x8.
Will the foundation hold it, which I am going to do as follows: drill 1.4-meter holes around the perimeter with an earth drill at a distance of 2 m from each other, lower the tied reinforcement into them and fill them half with concrete. Next, dig a ditch 0.7 m deep and 0.5 m wide between them, put the tied reinforcement there and tie it with the unfilled half of the pillar reinforcement.
Then use a mixer to fill this entire perimeter with concrete. Latitude - middle zone of the Russian Federation, south of Moscow, freezing depth 1.2 m, normal soil - loam. Will such a foundation support the above house if it is built from expanded clay concrete? What should you pay special attention to during construction and what “pitfalls” might there be?
Hello, Maxim!
Loam is not the worst, but also far from the best option for construction - it has pronounced heaving properties, which forces one to take measures to counteract this effect. The choice of this type of foundation is precisely designed for this.
Concrete pillars, poured below the frost level, will reliably support the load of the walls, and the tape tied to them will negate the risks of horizontal displacement that are characteristic of columnar supports.
To increase counteraction to the influence of ground heaving, especially in winter, it is advisable to take additional measures, namely:
- Instead of drilling pits, it is better to dig holes of larger diameter and build a conical formwork that expands downward to fill the pillars. The same applies to the shape of the poured concrete strip. This form of load-bearing structures will significantly reduce push-out loads during soil heaving in the vertical plane;
- Before pouring the binding tape, it is advisable to pour a compensation cushion under it with a layer thickness of 10-15 cm from crushed stone of a fraction of approximately 20-40 mm. This will further reduce the buoyant effect when the soil swells;
- It is a good idea to cover the walls of the concrete strip and posts with a low friction material. If this is done, the swelling soil will easily slide along the walls of the foundation, affecting it less. For these purposes, bitumen mastic is suitable, which in addition will serve as reliable waterproofing;
- It is advisable to insulate the soil along the perimeter of the base. To do this, at a depth of about 50 cm around the foundation, you need to fill a layer of expanded clay 20-30 cm thick or other similar material. The width of such a strip is 50-100 cm - the larger the better, but within reason. This will significantly reduce the depth of soil freezing under the foundation. It’s a good idea to put waterproofing under such insulation, for example, by putting roofing felt;
- Arrange a water drainage system - drainage. This measure is advisory, but in the case of high groundwater, drainage is necessary;
- Make a secure blind area around the entire perimeter of the house, at least 50 cm wide.
Regarding the question “Will such a foundation support a house if it is built from expanded clay concrete?” - the answer to it is obvious. Ten reinforced concrete pillars, poured to a depth of 1.5 m and connected with a concrete strip about 100 cm high and 30–40 cm wide, will support the weight of three such houses.
Laying the foundation for a house is one of the most important and costly stages of construction; ideally, it is entrusted to specialists. The total investment amount is about 30% of the total budget, and when contacting the appropriate companies, it often increases. It is important to understand the basic principles of creating an estimate and the factors that influence the cost, otherwise the customer risks getting a building made from low-quality materials and overpaying.
- How is the cost formed?
- Types of foundations and their descriptions
- Price of materials and work
What determines the price of construction?
The amount of costs is influenced by:
1. Type of construction, number of storeys, materials of walls, ceilings and roofing. The heavier the structure is erected, the higher the requirements for the foundation.
2. Soil parameters: groundwater level, freezing depth, bearing capacity, uniformity of layers. This factor is one of the most important; it determines the type of foundation chosen, the depth of its laying, the grade of concrete or the thickness of pile structures, the need for its protection, reinforcement, and drainage. When constructing critical and residential facilities, analysis of the soil condition is a mandatory stage; it is carried out even before drawing up the project.
3. The presence or absence of a basement in the house plan. In some cases, it is better to abandon the underground floor or basement; with high groundwater level, all measures to organize drainage may not be enough, and the costs of waterproofing increase significantly.
4. The quality and cost of the building materials used.
5. The need to use special equipment: lifting FBS during laying, concrete pumps, escalators, machines for screwing in piles.
6. Additional factors: remoteness of the site (affects transportation costs), presence or absence of electricity at the site, limitation in construction time.
Types of foundations and prices for them
The type of foundation is selected taking into account the first three points listed above: number of floors, materials and weight of a 10 by 10 house, geological and climatic conditions and the need for a basement. In this case, one of the following options is laid down:
1. Monolithic slab - a base suitable for almost any soil with the same slope on the site. The area of the base allows it to withstand maximum weight loads; the only drawback is the high construction costs; the maximum cost of pouring a foundation is observed when there is a basement in the project or a deep slab is laid.
2. Columnar foundation: prefabricated from FBS or vertical reinforced frames poured with concrete. Suitable for houses with a weight not exceeding average.
3. Strip monolithic foundation: shallow (50-70 cm) is selected when building on stable soils, deep (30 cm below the freezing level at least) - if a basement or plinth is needed, heavy materials of load-bearing structures. The cheapest and most versatile option, optimal in all cases, with the exception of very heaving soils.
4. Belt prefabricated. It is selected with a reduced time frame; when laying FBS, there is no need to wait 28 days for the concrete to gain strength. Restrictions include operation on peat bogs and other soils with low bearing capacity. A prefabricated foundation is 20-30% inferior in strength to a monolithic strip and loses in terms of efficiency: lifting equipment is used to install FBS.
5. Pile. The installation of metal supports is carried out quickly, within a day or two and does not depend on weather conditions; this option is suitable as a foundation for a house on a slope (allowable difference is up to 2 m), construction on highly frozen soils (and any other soils, with the exception of rocks) ). The disadvantages include high costs for purchasing piles, the need for special equipment, and restrictions on the number of floors. In this case, the lower part of the support must necessarily reach a stable layer; in some cases it is better to abandon this type of base.
The cost depends primarily on the volume of the tape. The length of the structure must be taken into account not only under the external walls, but also under the load-bearing partitions. The simplest calculation of the foundation using an online calculator shows that with a building size of 10 × 10 m, a standard tape width of 40 cm, a height of 70, 28 m3 of concrete, up to 240 kg of reinforcement, up to 3 m3 of lumber for formwork, at least 4 m3 of crushed stone will be required and 6 – sand for filling the pillow.
The recommended grade of concrete is not lower than M250; taking into account this condition, the cost of the material when purchasing a ready-made solution reaches 135,000 rubles, and when preparing it yourself - 90,000 (you will need to rent or purchase high-performance concrete mixers). In a similar way, it is determined how much the foundation for a 10×10 house costs when the tape is laid deep; in this case, it is important to take into account the need for waterproofing and insulation.
When laying a slab, the volume of soil removed is important. It is extremely difficult to dig a 10×10 pit below freezing depth without using special equipment. The second feature is the need to fill the slab base without interruptions. The thickness of the slab depends on the weight and number of storeys of the house: from 200 mm with single-row reinforcement for single-story buildings, at least 500 and a double-row frame for multi-story buildings. As a result, the minimum cost of a deep slab foundation with a standard thickness of 30 cm is 440,000 rubles.
When arranging a pile-type foundation, specialists are involved to draw up a diagram and select piles. The minimum number of screw supports for a one-story house is 25 pieces (with a diameter of at least 110 mm, a length of 2.5), for a two-story house it is increased to 36 (or piles with a larger cross-section are used). Installation of one support costs 350 rubles, but the final costs increase due to the need for test drilling, the need for supports, filling internal cavities, welding the heads, testing and strapping. The minimum cost of a foundation on screw piles for a building size of 10x10 m is 95,000, with the placement of thicker supports and a grillage - 215,000.
Cost of services for turnkey construction
*the cost of a deep strip foundation when placing turnkey floor slabs reaches 1,000,000 rubles and more.
The underground foundation of a building is the most significant and important structural element. The service life of the building, its thermal insulation characteristics, the level of indoor humidity and a healthy atmosphere depend on how correctly the calculations were made and how carefully the technologies were followed when laying the foundation.
Despite the apparent simplicity of the issue, the foundation for a one-story house must be carried out in strict accordance with design calculations and the use of design materials.
Factors affecting burial depth
The depth of placement depends on the type of soil, the mass of the structure
To determine how deep the foundation should be, it is necessary to study the operating conditions of the future structure. Calculation of the technical characteristics of the base is made after:
- work was carried out to study the soil at the construction site;
- the landscape has been studied or a construction spot has been cleared;
- a building plan has been drawn up, defining the area, weight of walls and ceilings.
At the stage of studying and collecting data about the location of the future building and the quality of the soil, the following parameters must be determined:
- soil type;
- average annual precipitation;
- groundwater level;
- depth of soil freezing;
- altitude differences in the terrain of the site.
Taking into account the design features of the house, its weight, the presence or absence of an underground or basement floor, they choose the type of foundation and calculate the depth to which to dig the foundation for the house.
Depending on climatic conditions, the size of the trench will vary.
The colder it is, the more seriously you need to approach the issue of installing the foundation.
The depth of the foundation is always greater than the level of soil freezing: in southern latitudes a depth of 60 cm is sufficient, in northern regions it will be necessary to go at least 1.5 m deep.
Soil definition
There are several ways to determine the type of soil
The type of soil has a significant influence on the depth of the foundation.
The table describes 5 types of soil:
This classification is included in the standards for checking the stability of underground foundations.
The degree of frost heaving is determined based on the level of natural soil moisture and the position of groundwater during the period when freezing begins.
The depth of the foundation for a garage, gazebo or other light building on heaving soils should be calculated especially carefully. If the depth level is insufficient or there is an error in the thickness of the base, soil with a high degree of frost heaving will squeeze the base out of the ground during the freezing period.
Terrain and types of foundations
In addition to the type of soil, it is important to understand both the evenness and uniformity of the topography on the building site. Sites with a slope must be leveled.
If it is not possible to level, then the minimum foundation depth is calculated taking into account the lowest point, and if there are large elevation differences in the area, then the type of foundation is selected either mixed or pile.
In practice, there are 4 main types of building structure:
- columnar,
- pile,
- tape,
- slab
Columnar base
This type of base is good for use on a small budget.
Pillars as a foundation for a house are the most budget-friendly solution, so they are often used for garage construction or for a one-story country house.
They are made from blocks, bricks or by pouring into formwork. Thanks to the use of technological materials, this type of base is time-consuming.
Waterproofing and a sand cushion are laid at the base of each pillar. Supporting elements are placed in places of the greatest vertical load: the corners of the house and the intersection of load-bearing walls of the structure. It is very important that the pillars are strictly vertical. With this type of foundation, the depth of the foundation for a one-story brick house is no more than 0.8 m, of which 30 cm is the cushion and waterproofing, and 0.5 m is the height of the pillar.
Piles
What is a pile foundation? When constructing this base, metal pipes with a blade at the end are screwed into the ground like self-tapping screws. Piles simultaneously support the building and distribute the load on the ground from the weight of the structure. The blade at the end of the pile prevents the structure from being squeezed out of the soil during freezing and heaving.
Such a foundation arrangement is especially relevant in the northern regions, where, due to climatic conditions and during winter freezing, the issue of squeezing out the foundations of light buildings and structures by heaving forces arises. In such conditions, piles are suitable both as a foundation for a garage and as a foundation for a one-story brick house.
For light buildings, metal bladed piles are used
How to determine the depth of foundation on piles? The depth of freezing is determined by the trenching method. The drill is screwed in to such a depth that the blades are below the freezing level in dense layers of soil.
The piles can withstand a tensile load of up to 330 Pa. In this case, the maximum pressure force during heaving is 0.2 Pa.
Metal blade piles are suitable for the construction of lightweight buildings. The technology of bored piles has been developed for heavy buildings.
The great advantage of such a foundation is that work on its construction can be carried out at any time of the year in any climatic conditions.
Strip foundation
The strip foundation design is a monolithic, solid, inextricable concrete pour, usually with internal reinforcement.
The foundation is placed under all walls of the building, including partitions that carry vertical loads. Along the perimeter, the base has the same cross-sectional dimensions.
The foundation strip forms a continuous contour
Depending on the type of soil and the mass of the building, various shapes are poured:
- rectangular;
- trapezoidal;
- T-shaped.
The integrity and continuity of the base contour ensures uniform distribution of vertical and horizontal loads. This explains the strength, reliability and demand for this type of foundation. In addition to the shape of the base, it is important to determine at what depth to make a monolithic strip foundation. For a detailed presentation on strip foundation construction technologies, watch this video:
Shallow design is not suitable for heavy buildings
Depending on the weight of the building, the level of soil freezing, the location of groundwater and the type of soil, the depth and types of strip foundations can be different:
- shallow with a depth of no more than 0.6 m. The device is supposed to have a movable base, subject to soil heaving. Not suitable as a basis for the construction of heavy buildings;
- buried - a reinforced concrete monolithic frame laid below the freezing level of the soil. Used for buildings with basements that have a large mass.
Plate
Slab foundations can be installed on any type of soil
Like tape, a monolithic slab can be recessed or not. In the first case, the slab is poured into a pit and has high ribs. The main disadvantage of such a device is its high cost. But this is the only type of foundation that has no restrictions on the type of soil.
How to calculate the laying depth, and what should the slab be? The heaving of the soil does not affect the condition of the building on this basis, therefore this distance is determined based on the operational requirements for the building. For more information about building the foundation, watch this video:
The monolithic slab is a floating solid foundation and its installation is possible even on swampy or peaty soils, where the groundwater level is quite high.
The summary table shows the types of foundations, soil types and weight of the structure
| Columnar | suitable for heaving soils | small-sized, lightweight | ||
| Pile | except rocks | suitable for non-heaving soils | the device is permitted at large freezing depths | any, without underground floor arrangement |
| Tape | sand of coarse and medium fraction, coarse, cartilaginous | suitable for heaving soils | lungs | |
| Monolithic slab | no limits | suitable for heaving soils | any heavy |
In case of mass construction, the calculation of the depth of construction is carried out by specialists at design institutes. More often, during individual self-development, the question arises: how to calculate the foundation for a garage, bathhouse or one-story cottage?
After receiving all the necessary data on the soil and the weight of the building, a final calculation is performed and the depth of the foundation is determined.
The depth, although within the same limits, will nevertheless always be different. On the same site, the foundation for a one-story or two-story brick house will differ significantly.
Each calculation is purely individual. If it is not possible to contact specialists, you can enter the data into an online calculator and find out the recommended dimensions adjusted for freezing depth. For more information on calculations, watch this useful video:
- Any foundation is laid below the soil freezing level by 10%. If the freezing value is set to 70 cm, then the depth of the hole under the base should be 77 cm.
- For loose soils in temperate climates, it is better to use a strip base with a laying depth of 0.5 to 1 m.
- In the northern regions with slightly heaving soils, a foundation buried up to 2 m is made.
- In swampy areas or on clay, a slab would be an ideal option, and the depth of burial can reach 2.5 m, which allows you to make a basement.
The basic rule when calculating the foundation: a competent and reliable foundation is the key to a long service life of the building. It is worth noting that overdoing construction is also fraught with consequences, as is saving. A pit dug below the required level will not make the house more reliable, but will increase the consumption of materials and the area that will be negatively affected by soil and groundwater.
The construction of the foundation of a building is an important stage in construction. The strength of the entire structure depends on how correctly the base is laid.
To build a reliable and durable foundation for a one-story house, you must be guided by SNiP regulations: 2.02.01-83 “Foundations of buildings and structures” and 23-01-99 “Building climatology”.
Features of foam block material
Foam concrete blocks are made from cellular concrete by pouring it into special forms. The resulting layers are cut into elements suitable for building houses.
Types of foam blocks
The material is divided into three types depending on density. For private construction the following are relevant:
- structural elements of grades D1000-1200;
- structural and thermal insulation blocks of grades D900-500;
- thermal insulation segments of grades D500-300.
The high density of foam concrete allows the construction of a two-story building with a reinforcing belt.
Properties of building materials
Foam block buildings are becoming relevant for owners of suburban areas. This is facilitated by the properties of the material:
- a unique “breathable” structure, thanks to which sweating of the walls is eliminated;
- the ability to retain heat in winter and provide coolness in summer;
- profitability - due to heat conservation, home heating costs are eliminated;
- good sound insulation;
- environmental cleanliness;
- ease of processing and strength of walls.
Low cost elements based on sand, water, cement and special foam. Small costs for construction consumables allow you to invest more money in arranging a high-quality foundation for your home. 
Compared to buildings made of bricks, foam block buildings are lighter. If a square meter of a brick wall weighs 1.8 tons, then foam blocks have a mass of 0.9. Therefore, it would be inappropriate to construct massive foundations. For a dwelling made of foam block, a monolithic strip, slab or pile base is sufficient. Regardless of the type of foundation, it is worth considering the criteria for its construction and design.
Depth selection: influencing factors
The depth of the foundation for a one-story building is determined through accurate, competent analysis and calculation, taking into account the characteristics of the structure and the environment. The choice of recess is influenced by the following indicators:
- degree of soil freezing;
- climatic features of the region;
- groundwater level;
- quality of the soil surface, occurrence of layers;
- availability of design additions (basement, ground floor, garage);
- type of foundation.
Laying the foundation for a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks is carried out above the groundwater level and below the freezing layers. Correct calculations ensure the reliability and durability of the building, the main building material of which is expanded clay block. 
What influences the choice of base height?
The height of the foundation for a one-story house is set taking into account the following factors:
- Relief features of the land plot for development. If there are small slopes, the depth of the foundation for a one-story house increases; in areas with seismic activity, additional measures must be taken to increase the stability of structures. The full picture is provided by calculations based on geodetic data.
- Design features of the building and its purpose. Construction is carried out with or without a basement floor.
- Level of groundwater passage.
- The presence of nearby buildings and the type of supporting system used.
- The composition of the soil, the presence of various voids, bedding in layers and other features.
The ground part of the basement for a house made of timber can rise several meters above the ground, unlike heavy brick buildings.
Varieties and types of soils
When calculating how deep the foundation should be installed for a one-story block house, you should take into account the types of soil. It happens:
- non-heaving – rocks, sand;
- heaving – sandy loam, loam, clay;
- slightly heaving – a varied mixture.
The best type for the construction of residential buildings from expanded clay concrete is considered to be a non-heaving type, characterized by high strength and the ability to withstand various loads. For it, the optimal foundation depth is 0.5 - 1 m, for mixed - 0.5 - 1.25 m, for clay - 1.2-1.5 m, without taking into account other factors. 
Types of foundations for one-story buildings
The foundation for a house made of blocks is the load-bearing part of the structure. How reliable and durable the house will be depends on its type. For the construction of a block one-story building, 3 technologies for laying a monolithic system are used: a traditional strip base, a columnar structure and a slab system.
Laying depth of strip foundation
For one-story buildings, with heaving soil, the laying depth of the strip foundation is 60 cm for the shallow type. The design resembles load-bearing floating systems lying under the sole and capable of withstanding soil movement.
The buried type is performed below the freezing point of the soil. The laying depth reaches 1-1.5 m. A monolithic tape with reinforcement is constructed. This look is typical for the construction of massive brick and block houses.
Experienced craftsmen note that the width for the foundation should have a size that exceeds the thickness of the walls by 5-10 cm. This will ensure the reliability and stability of the base of the building. 
Pile foundation level
The strength of the building depends on the depth of the base. For the construction of one-story buildings, a pile foundation is often used.
The method of constructing foundations using piles gained popularity due to the use of drilled rods. A bored construction is a universal way of arranging a basement floor and has several advantages:
- Used on terrain with characteristic slopes.
- Does not require preliminary soil preparation or clearing of the construction site.
- It is economical. Laying is carried out using a minimum amount of building materials.
- The pile system is not a continuous structure, which ensures unhindered communication under the building.
- The construction is carried out without the use of special equipment.
- The laying of the pile foundation can take place one at a time, in contrast to the strip foundation, where concrete must be poured immediately along the entire perimeter.
What will be the installation depth of the pile foundation - the support for a one-story house built from blocks must be 10-15% below the soil freezing level. This will allow the core structure to easily carry the loads of the building. On heaving soils, to ensure the strength of the system and eliminate structural deformation, the piles are additionally reinforced. 
Features of installation of a slab base
The monolithic system is stable and reliable. The slabs are a solid concrete base. To lay them, it is necessary to prepare a pit and clear the construction site.
The slab is laid to a depth of 60-100 cm, on a sand and gravel bed. The foundation can withstand heavy loads of buildings.
How to calculate the optimal depth for laying a plinth: recommendations from experts
After determining the type of foundation and analyzing the parameters characteristic of a particular area, you should calculate the optimal depth for installing a solid foundation for a one-story building.
Each calculation is individual, but its implementation requires compliance with the following recommendations:
- any type of supporting structure is laid on average 10% below the freezing level of the soil layers. For example, the freezing point is 100 cm - the trench is dug at a depth of 110 cm.
- for loose soil in a temperate climate zone, it is recommended to equip a shallow foundation (monolithic or made of blocks). The slab is deepened by an average of 45-100 cm.
- for a weakly heaving mixed group in harsh cold latitudes, a structure is used that is dug in at 1-2 m.
- The foundation for a one-story block house using two laying technologies is characterized by reliability and strength. For example, a strip base with the addition of reinforcing rods.
- For swampy and clayey areas, it is planned to lay a monolithic slab system with piles. The base is installed at a depth of 2.5 m.
 Some builders advise constructing the foundation with a “margin”. But this is not always the right decision. Firstly, it will still be necessary to carry out land work, and secondly, financial costs are required. The feasibility of its implementation is excluded on permanent dense soils, with low seismic activity, in temperate climatic zones.
Some builders advise constructing the foundation with a “margin”. But this is not always the right decision. Firstly, it will still be necessary to carry out land work, and secondly, financial costs are required. The feasibility of its implementation is excluded on permanent dense soils, with low seismic activity, in temperate climatic zones.
To construct a supporting structure for a one-story house, builders often use strip foundations. Other types of bases have gained popularity due to their cost-effectiveness and quick DIY implementation. To build your reliable home, it is better to resort to the use of several technologies in the construction of a durable and strong foundation.
Foundation depth for a one-story house
Today, do-it-yourself construction of a variety of non-residential buildings, as well as houses and country cottages, has become widespread.
Building a house has some difficulties due to many parameters that must be taken into account before planning the foundation; how long the house will last depends on them.
Laying the foundation is the most important part of construction, and its depth determines the strength of the entire further structure.
For any building, the depth cannot be simply determined by eye; many calculations are needed here, and first of all you need to pay attention to:
- groundwater flow level;
- climatic features of the area in which the house will be located;
- soil freezing depth;
- total building load and construction materials;
- selected foundation type.
The first thing you need to know when calculating the depth of the foundation is that it must be laid below the freezing level of the ground so that the foundation does not deteriorate due to repeated freezing and thawing.
It should also be located above the level of groundwater flow, which is a strong destructive force for the foundation.
An example of a finished structure for a one-story house without a basement is presented below.
Types and varieties of soils
When calculating the depth, you need to immediately find out which soil will be under the foundation of your house. They are:
- heaving, that is, clay, loam, sandy loam;
- non-heaving: sand, rocks;
- slightly heaving soils - various mixtures.
The most optimal soil for construction is non-heaving soil, as it is durable and can withstand any load. You can see an example of such soil below.
You can find out such data by contacting specialists and taking a soil sample from the site.
Non-heaving soil
In accordance with the data obtained, the first calculations can be made, following which the optimal depth for non-heaving soils will be 0.5-1 meter.
For clayey soils - 1.2-1.5 meters, for mixed soils - from 0.5 to 1.25 meters, depending on how mobile the soil is and what percentage of the heaving mixture it contains.
Determination of groundwater level
In determining the second parameter, you can also turn to specialists or try to find out this yourself using special wells called shufrs.
They are dug out at the site of future construction, their minimum depth is 2-2.5 meters.
Using such a well, you can determine the depth of soil freezing and the presence or absence of groundwater. An example of such a well is shown in the photo below.
Suffer for determining soil type
The terrain of the site for construction is also important, because it is easier to lay a foundation on a flat surface.
If the site is on a slope, then it will need to be either leveled as much as possible, or when laying the foundation, take the lowest point as the basis for measuring the depth.
After determining the soil and the absence of obvious presence of groundwater, you can think about the type of future foundation.
It also depends on the type of soil whether lateral reinforcement of the walls is necessary so that the foundation does not tilt over time.
Choosing the type of foundation according to the soil
The foundation itself directly depends on what depth is needed for your construction and on the type of soil being determined.
If it is not heaving, then you can plan a regular strip or columnar foundation, but if the ground is heaving or slightly heaving, then you will have to make a monolithic slab or pile foundation.
Let's consider the main types of foundations for a one-story house, taking into account the depth of foundation:
- Strip foundation, which can be either shallow (for light-weight wooden one-story buildings) or buried. This type is the easiest to install independently and the cheapest. If great depth is not required and the weight of the structure itself is small, then you can choose it.
- Pillars and piles can strengthen a strip or conventional foundation, while for a house that is lighter in weight, it is better to use pillars. If the materials for construction are brick or stone, then it is better to drive in piles that can withstand heavy loads, distributing the entire load-bearing weight over perimeter and deeply strengthened in the ground.
- A monolithic slab can be used in the case of heaving soils and in identifying groundwater.
This design is the most reliable and will withstand any impact and weight, but it will also be expensive and will be difficult to install yourself.
An example of such a plate is shown below.
Monolithic slab - base
Calculation of foundation depth
When you have finally decided on the type of soil and foundation, you can make a final calculation, which will determine the depth of the foundation for a one-story house.
Some try to make the foundation “with a reserve”, that is, to deepen it more than the required level for reliability.
But this will only be an extra financial cost and time-consuming work, and if all calculations are made correctly, then no reserve is required.
Any foundation is laid based on the level of freezing of the ground and is laid 10% lower, that is, if the freezing depth is 1 meter, then it should be laid to a depth of 1.1 meters, this will be enough.
If the climatic conditions in the region of construction are moderate and the soils are loose, then it is most appropriate to lay a shallow strip foundation, which is easy to do with your own hands and will be durable.
It can be either monolithic with a self-filled solution, or prefabricated with ready-made blocks.
By average standards, such a foundation is laid to a depth of 45 cm to 1 meter. Such a foundation looks like the one shown below.
Ready strip foundation
In more severe winter conditions or when the soil mass is heterogeneous, it is better to make a deeper and more reliable foundation, the depth of which can be from 1 meter to 2 meters.
For a one-story house made of ordinary brick, a recessed strip foundation with pillars that will strengthen the entire supporting structure would be quite acceptable.
If the area is swampy or very clayey, then you will have to lay a monolithic slab with piles, even if the structure of the house itself is light.
This will entail considerable financial costs, but you don’t have to worry about the reliability of the design. This foundation can reach a depth of up to 2.5 meters.
Choosing materials for the home taking into account depth
The most economical option these days are wooden one-story country houses, in which you can also make an attic.
When choosing such materials, the house will be quite light and the chance of destruction of the foundation will be minimal, so you can choose a shallow depth and lay the foundation yourself in case of any difficulties.
This building looks like the photo below.
Wooden one-story house
One-story houses made of foam blocks are also easy to build and do not require a large laying depth, but they must be wider, since the wall in such houses should be about 60 cm for heat resistance.
Brick or masonry requires that the laid foundation can withstand a large load, so it is advisable to choose both a large laying depth and reinforcement with piles.
This foundation looks like the image below.
Pile foundation
Considering all these factors, we can say that the depth of the foundation for a one-story house can be very different, but all the above factors should be taken into account for the reliability of the structure.
The main reference point remains the depth of soil freezing, which underlies all calculations of deepening.
Video calculations of the foundation depth of a one-story house
In the next video, experts will tell you what rules must be followed when calculating the depth of the foundation, which will help you correctly determine all the parameters, and you will be able to independently build your house, which will last for a very long time.
Residential buildings with one floor have been popular among craftsmen for many years. They are economical, easy to design and build. To build a foundation for a one-story house, you need almost half as much building materials as for a two-story building.
Types of structures
Before starting construction work, it is necessary to develop design documentation. These are diagrams and drawings that will help you choose the optimal type of supporting base. For a one-story house you can make the following foundation with your own hands:
- Monolithic;
- Columnar;
- Pile;
- Tape;
- Columnar-flying.
Monolithic- this is a type of construction when a large trench is dug under the future house, repeating or slightly exceeding the area of the building itself. It is compacted with sand or crushed stone cushions, and then filled with cement mortar. Sometimes foam concrete or gas silicate is used, but most often such materials are used in the construction of a country house. Sometimes such a support is built by installing a ready-made monolithic slab of concrete and reinforcement, which significantly reduces construction time.
Photo - monolithic foundation with a sole
Columnar- a very popular type of base, which is considered one of the most economical options. It can be made using poured pillars, installing supports from foam blocks or bricks, and also driving concrete foundations into the ground. Mainly used for wooden houses, block or residential premises made of timber.
Pile- an analogue of columnar, but it is used on problem soils. At first glance, the unreliable support system copes well with high loads - on average, one pile can carry up to 18 tons. Pile construction is used on sand, rocky and clayey soils, and houses are also built on swampy soils using this system.
Tape the foundation for a one-story residential building is, in most cases, the ideal solution. Due to the combination of high load-bearing performance and economical consumption of building materials, most home craftsmen choose just such a system for their home. The strip type of base can also be made from block bricks, aerated concrete, foam concrete, cement mortar and reinforcement bundles.
Photo - strip foundation
Columnar-ribbon or strip pile - this is a combined type of load-bearing structure for a private house. In most cases, it is a simple structure with point supports, which are additionally reinforced with a grillage. But some craftsmen use a more complex system for their buildings. The technology of internal pillars is the principle of building a foundation, when first a trench is dug, suitable in depth for the foundation. Afterwards, additional cylindrical holes are dug in it, and they, together with the upper trench, are filled with solution.
Photo - high strip foundation
All types have their advantages and disadvantages; to choose the right option, be sure to consult with specialists.
Video: foundation on screw piles
Technical specifications
Before starting construction, you need to know what the height and depth of the foundation for a one-story house should be. These dimensions can be calculated with only initial data on the planned thickness of the walls and the material of the buildings in general. First, you need to calculate what bearing capacity the soil has in your region.
Photo - shallow foundation
You will find this indicator in the geological bureau of your region. Then you need to calculate how much pressure the building exerts on the foundation. To do this, all loads are summed up: floors, roofing materials, walls, doors, windows, insulation, etc. The resulting number is multiplied by a conditional coefficient of 1.3 - this is the approximate pressure that will be exerted by furniture and residents. A certain number of tons will come out - this is the mass of the building.
Next, you need to calculate the dimensions of the foundation. Here, each type has its own characteristics. For example, if with pile and columnar everything is very simple (the selected support and the weight of the house is divided by its load-bearing capacity), then with strip and monolithic it is more complicated. The minimum permissible depth for a foundation for a one-story house with an attic is 30 cm for rocky soil, 60 for sand and 85 for loam. For greater reliability, similar indicators can be taken for a monolithic slab, but in this case it will be very expensive. This is a normally buried foundation; for a wooden structure or frame house you can make a shallow foundation, but its parameters need to be calculated more accurately.
After calculating the depth, you need to decide on the width. The minimum permitted width of a strip foundation is 25 cm, and it is very important that the sole, i.e., the base of the support system, is slightly wider than the top. Of course, the thickness of the walls plays a big role here. Masters advise taking a size for the width of the foundation that is 5-10 cm greater than the thickness of the walls. You can choose the right proportions based on the finished building design.
Photo - foundation project for a one-story house
How to build a foundation
When the width, thickness and height of the foundation for a one-story house are known, you can begin construction. Let's look at how to make a strip support system:
- You need to make a trench that is the same size (or slightly smaller) than the future tape. Its walls should be reinforced with wooden boards - this will protect the system from destruction;
- Next, we install the fittings. You can build it with a checkerboard pattern or tie several bundles and secure them together. It is advisable to install the rods in the center of the trench;
- Afterwards you can proceed to pouring the foundation of the system. It is advisable to carry out all work with concrete in one day so that the base hardens evenly;
- The structure will dry from 3 days to a week, depending on weather conditions.
Insulation
Many projects imply that it is necessary to insulate the foundation for a one-story house (especially with a brick, foam concrete or high pile foundation). For these purposes, you can use an additional layer of cement mortar (fur coat), or take care of thermal insulation in advance. To do this, before starting pouring, a waterproofing film is installed on the sand cushion.
Photo - insulated foundation
Regardless of the height of the foundation, it wraps around its entire area. Afterwards, the structure is poured, and another layer of insulation is installed on top of the finished base. This can be economical polystyrene foam or more expensive foam concrete. This arrangement of the facade will protect the residential building from heat loss and flooding.
expand
Dear! Tell me how to properly pour the foundation for a one-story house with an attic 6h9 in the country
Reactions to the article
Show previous comments (showing %s of %s)
Show new comments
Showing all comments: 4
Facebook comments
Full list of topics « Previous topic
Next topic » This item is in every kitchen, but only 4 out of 10 housewives use it 100%! May 10, 09:01 0 0 Apply this to scars, wrinkles or blemishes on your skin and enjoy how quickly everything will disappear! May 10, 07:01 0 0 House invisible in the landscape: admire the starry night May 9, 23:01 0 0 Little gray: apartment with a mezzanine bedroom (23 sq. m.) May 9, 21:01 +2 3 Interesting storage systems in bathroom May 9, 19:01 +1 0 Stereoscopic wallpaper: ultra-realistic illusion of a three-dimensional image on the wall May 9, 17:01 +1 0 Smart gadgets for the kitchen of 2018 May 9, 15:01 0 0 Persistent windowsill stains will disappear quickly and without trace May 9, 13:01 +3 1 Why does intelligence affect marital fidelity? May 9, 11:02 0 0 Who wants to spend half their life cleaning? May 9, 09:01 +4 0 Extraordinary house: “ribbon” with panoramic windows May 9, 07:01 0 0 Elegant modern classic for a family from Russia in London May 8, 23:01 +1 0 Villa in Moraira, on which billionaires are resting May 8, 21:02 -4 0 Quite a civilized reason why many people sprinkle salt on their threshold May 8, 19:01 +2 0 How to remove toxins and get rid of foot odor. 8 May, 17:00 +2 1
Nowadays, houses with attics are increasingly being built. An attic or attic floor is a room in the attic space, the walls of which are formed by the surfaces of the roof. The first to use this design was the Frenchman Francois Mansart back in the sixteenth century. Who would have thought that they would become so popular nowadays.
A house with an attic has its own characteristics compared to a simple house. The main one is the shape of the roof. For houses with an attic, gable, hip and hip roofs are mainly used.
What attracts people to houses with attics? Firstly, it’s beautiful, and secondly, it’s economical; you don’t have to build walls on the second floor. Also, such rooms have fewer windows than regular ones and this will reduce your costs.
Such houses can be built from any building materials: brick, wood, concrete. Thanks to different materials, a house with an attic can resemble either a castle or a fairy-tale tower.
Any construction begins with the foundation of the building. Let's figure out which foundation for the attic is better.
Foundation for a house with an attic
In the construction of private cottages, the following types of foundations are more often used:
- Tape;
- Columnar;
- Pile;
- Slab.
Each of them has both disadvantages and advantages for use as a foundation for a house with an attic.
The strip foundation completely follows the line of the load-bearing walls of the building. Such a foundation is made in the form of a concrete strip buried in the ground. These concrete strips are often laid on so-called concrete pads, thereby achieving greater stability.
A strip foundation is suitable for a house with an attic or a two-story house as it can withstand heavy loads.
The columnar foundation is used for the construction of light and small buildings and therefore it is not suitable for the construction of houses with an attic.
Pile foundations are mainly used on slopes and in very soft soil. It consists of piles installed vertically into the ground. Piles can be made of reinforced concrete, wood and asbestos.
Slab foundation is the most expensive type of foundation. However, it is worth the money spent on it. Such a foundation is particularly strong, since the load is evenly distributed over the entire soil area.
Foundation for a house with an attic
The foundation for a house with an attic is selected and calculated, taking into account the condition of the soil, the proximity of groundwater, the depth of freezing and the magnitude of the load.
It is best to order a foundation design from a design organization.
Mostly we neglect this and follow the advice of builders (good if they are professionals) or the experience of neighbors who have recently completed construction.
If the house is not located on a slope, a monolithic slab foundation is suitable for any type of soil.
A cheaper option is a strip foundation, which is a well-reinforced reinforced concrete strip located on a sand bed and following the contours of the building.
The choice of foundation type also affects whether the house will have a basement or not.
If you do not plan to make a basement under the house, then a shallow strip foundation would be appropriate. It is done with monolithic concrete in one day, so that there are no seams, and reinforced with 12mm reinforcement.
The base of the foundation is made of compacted coarse sand.
In view of all of the above, we can conclude that the foundation is one of the most important elements of your home. The strength and durability of your home will mainly depend on it.
It’s better not to skimp on the foundation and use the best materials you can afford. Because any miscalculations and mistakes when laying the foundation can result in serious costs for their alteration when the house is already built.
As they say, it’s better to measure seven times and cut once.
You can see the main mistakes when laying a foundation in this video: